North Dakota is divided into 53 small units of government called counties. The purpose of a county• Small unit of government that helps the state carry out its duties
• North Dakota has 53 counties is to help the state government carry out its duties.
Services provided by counties include protecting citizens, setting up elections, collecting taxes on property, building and taking care of roads, and clearing snow.

Figure 28. The Dickey County courthouse is located in Ellendale, the county seat. (Neil Howe)
Each county includes a town with a courthouse containing the offices of the county government. This town is called the county seat.Town with a courthouse containing the offices of the county government
The main governing body of a county is the County Commission.Main governing body of a county Either three or five persons are elected on nonpartisanPolitical parties are not involved in their election (no-party) ballots to serve part-time on this board. They oversee all of the business of the county.
Other county officials are also elected on no-party ballots. The sheriffPolice officer for the county is responsible for keeping law and order; the state’s attorneyLawyer who represents the state at the county level is a lawyer who represents the state at the county level; the county recorderIn charge of county documents is in charge of documents such as deeds;Document to show proof of land ownership the treasurerIn charge of the county’s funds (money) is in charge of the funds; and the county auditorBookkeeper for the county is the bookkeeper for the county.
Several county officials are not elected by the voters, but they are appointed by the county commissioners. Examples are the county superintendent of schools, who supervises schools that do not have their own superintendent, and the county agent, who provides advice and assistance in agricultural matters.
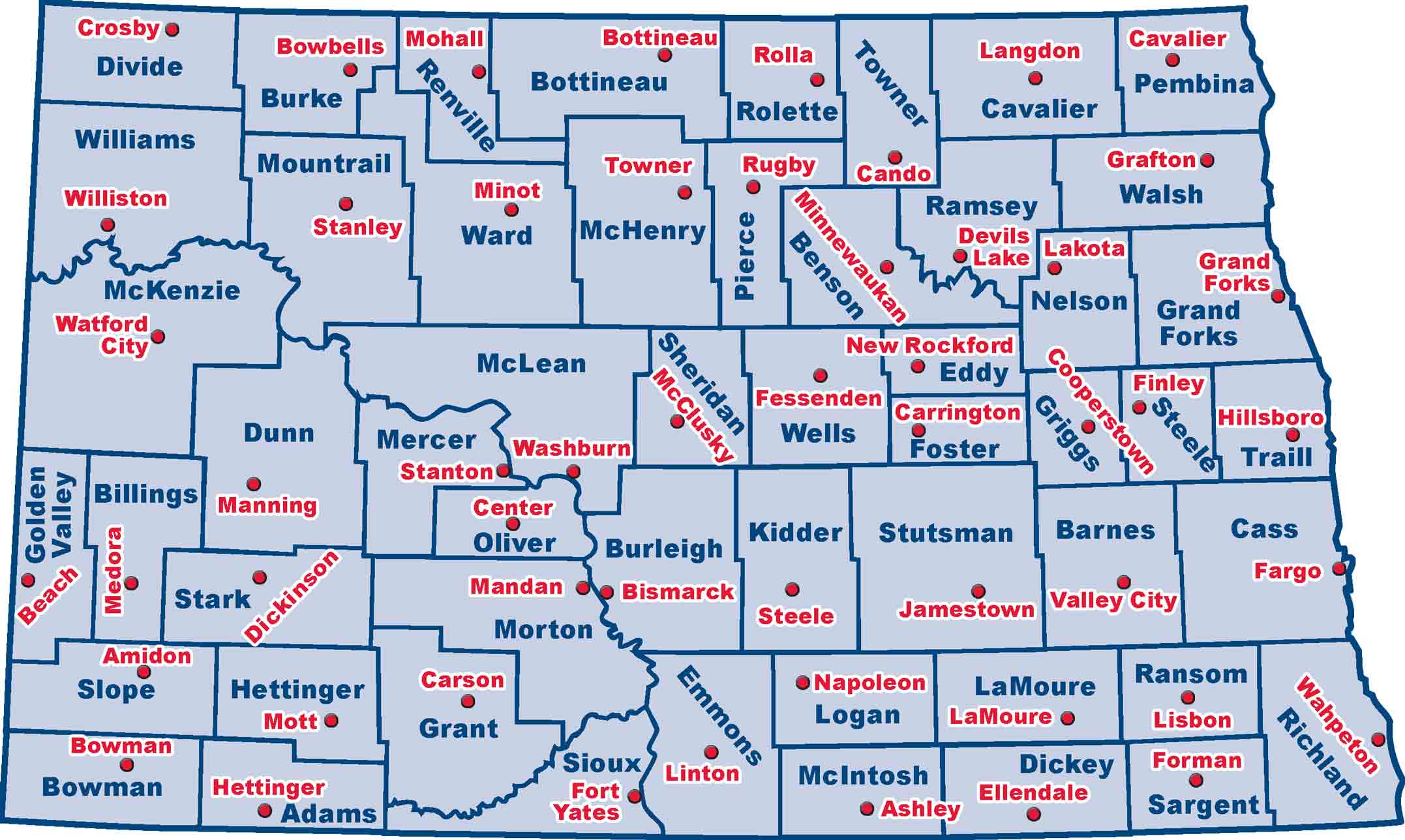
Figure 29. North Dakota has 53 counties. Each county (in blue) has a county seat (in red) where government offices are located. (SHSND-ND Studies)


