What solar power is:
- Solar power is a renewable resource because it will never be used up.
- Solar power is power created by changing the energy of the sun's rays into a useful form of energy.
The sun is a ball of gases – mostly hydrogen and helium. The core (center) of the sun creates energy in a process called nuclear fusion. It takes about eight minutes for light from the sun to reach the earth.
- Solar energy can be used in a variety of ways:
- Examples are providing heat, light, and hot water for homes; and generating electricity.
- Passive solar energy means that an object is heated because sunlight is warming it.
- Passive solar systems trap and store thermal (heat) energy directly from the sun.
- Solar thermal energy means concentrating the sun's rays to heat water or other liquids.
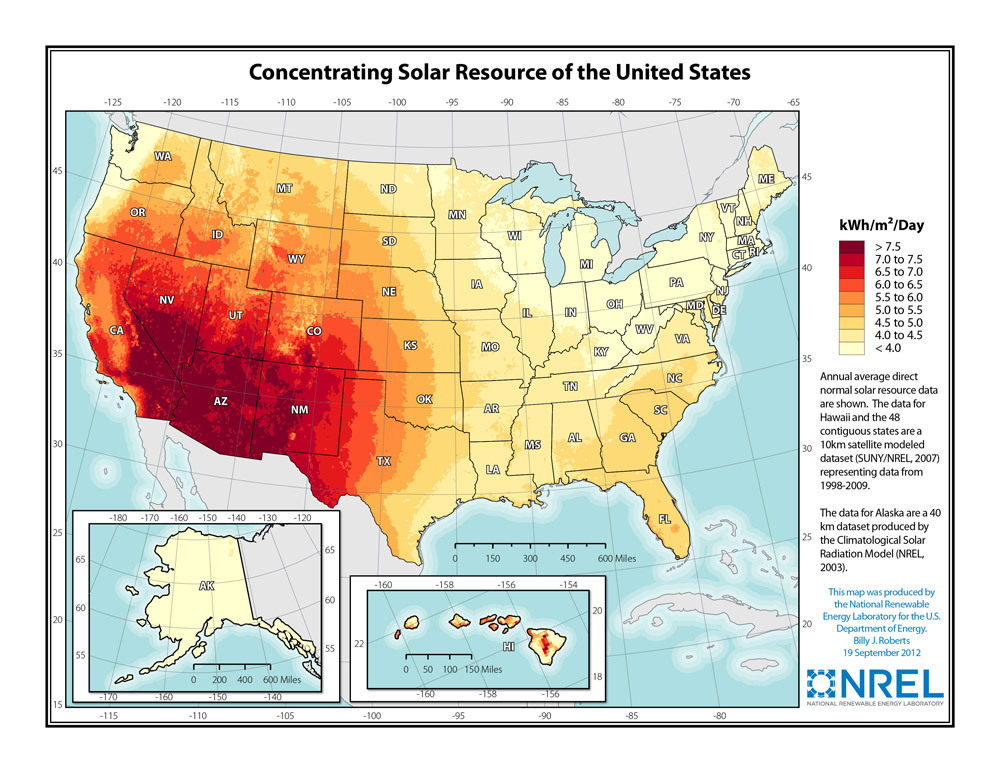
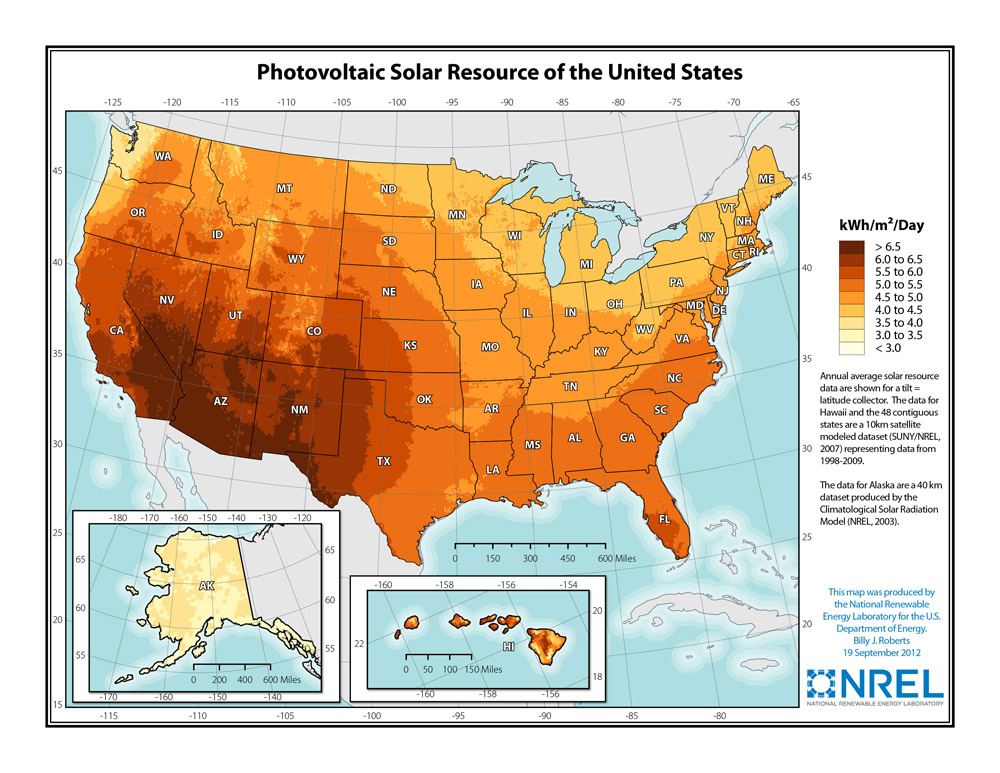
- Electricity can be created through a photovoltaic (PV) systemPhoto means light; volt is a measure of electricity. Photovoltaics (foe-toe-vol-TAY-iks), also known as PV, means solar electricity. or a concentrated solar power (CSP) system.
A PV system uses the sun's rays to create electricity, and a CSP system uses mirrors to concentrate sun rays to create heat that, in turn, runs a heat or steam engine.
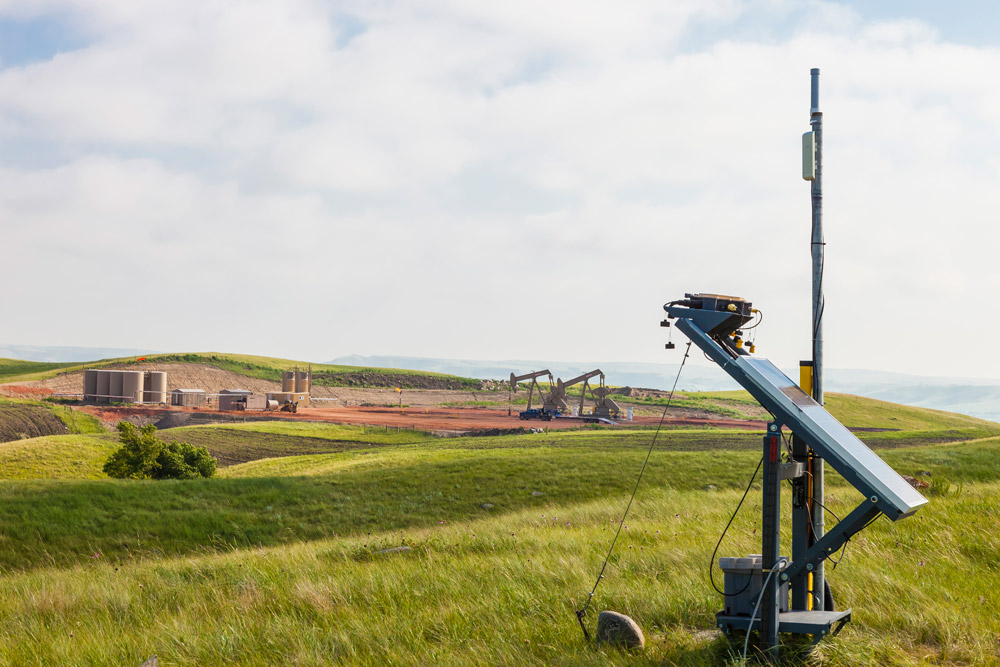

Solar Energy at work in the oil fields: Whiting Petroleum uses photovoltaic systems at oil well sites so that control room staff at natural gas processing plants can see production levels at any time.
Photo courtesy of Whiting Petroleum.
- A photovoltaic (PV) system has several parts:
- PV panels (solar panels) arranged in arrays (rows and columns);
- PV panels are groups of PV cell.
- Batteries
- An inverter that makes the electrical current useable;
- Wires and other parts
- PV panels (solar panels) arranged in arrays (rows and columns);
- Sunlight is made up of photons, which are particles of solar energy.
- When photons strike a photovoltaic (PV) cell, some of the photons are absorbed.
- The absorbed photons produce electricity.
Solar power in North Dakota:
- North Dakota has more hours of sunlight than any other state along the Canadian border, but unfortunately the state also has short days in the winter when electricity is in great demand.
- Solar energy is used in North Dakota for several purposes:
- For passive solar heat and daylighting;
- For solar thermal and hot water heat.
- To generate electricity by photovoltaic systems.
Daylighting means having a lot of windows, skylights, etc. placed so that natural light from the sun is used to help light the interior of the building.
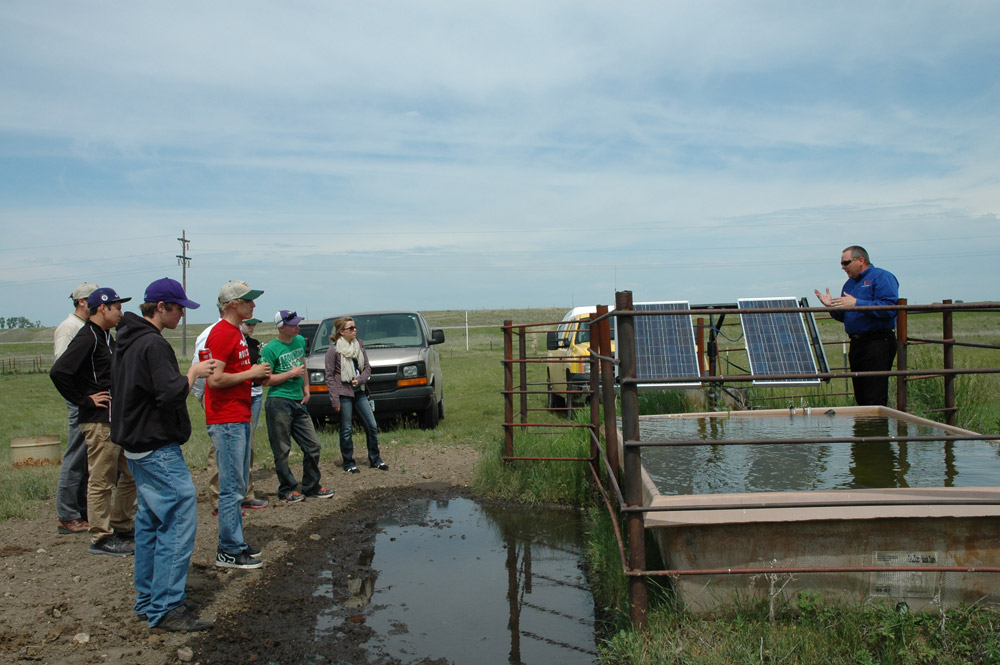
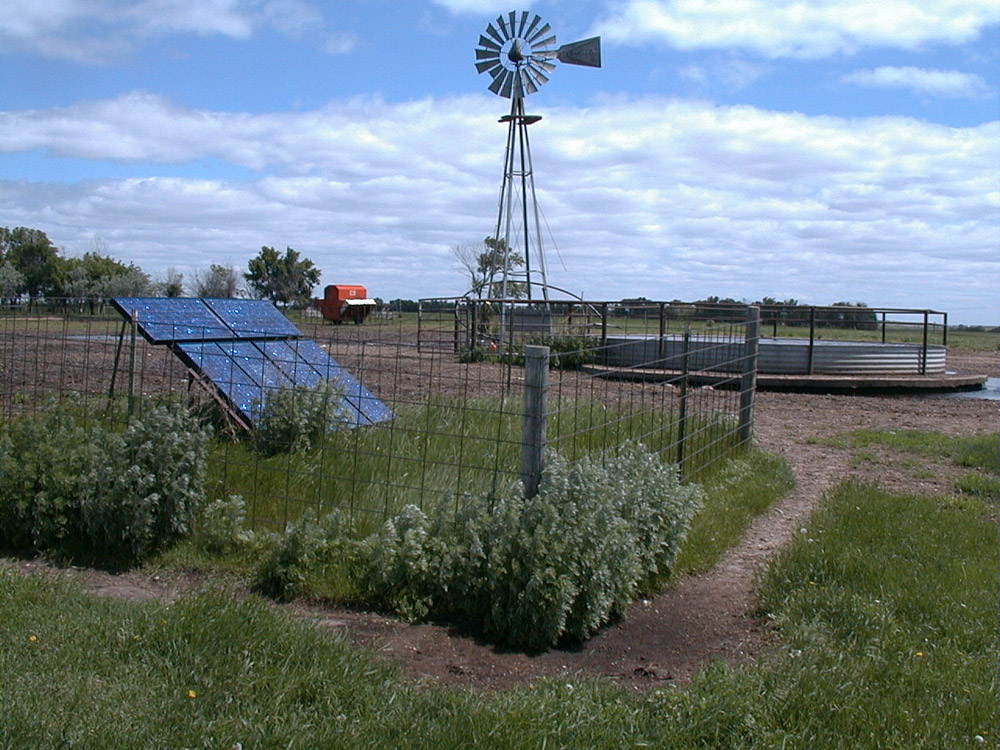
- Verendrye (ver-EN-dray) Electric Cooperative in Velva, North Dakota has the largest solar program in the state.
- This utility company owns more than 260 solar-powered water pumps.
- The solar water pumps are placed at wells in pastures that are far away from electrical lines.
- Using solar water pumps saves money for Verendrye Electric members.
- The solar panels cost about $800 to install, and installing electrical power lines can cost as much as $15,000 per mile.
- This utility company owns more than 260 solar-powered water pumps.
- Cass County Electric Cooperative in Fargo, ND, installed a 102-kW solar array in 2016, called Prairie Sun Community Solar. It is the first community solar project in the state and consists of 324 solar panels located on land owned by the city of Fargo.
- The North Dakota Department of Commerce supports the following solar energy programs:
- Photovoltaic lighting for signs at Cross Ranch State Park, Turtle River State Park, and the State Hospital at Jamestown;
- A photovoltaic water pumping system at Cross Ranch State Park;
How solar power affects the people of North Dakota:
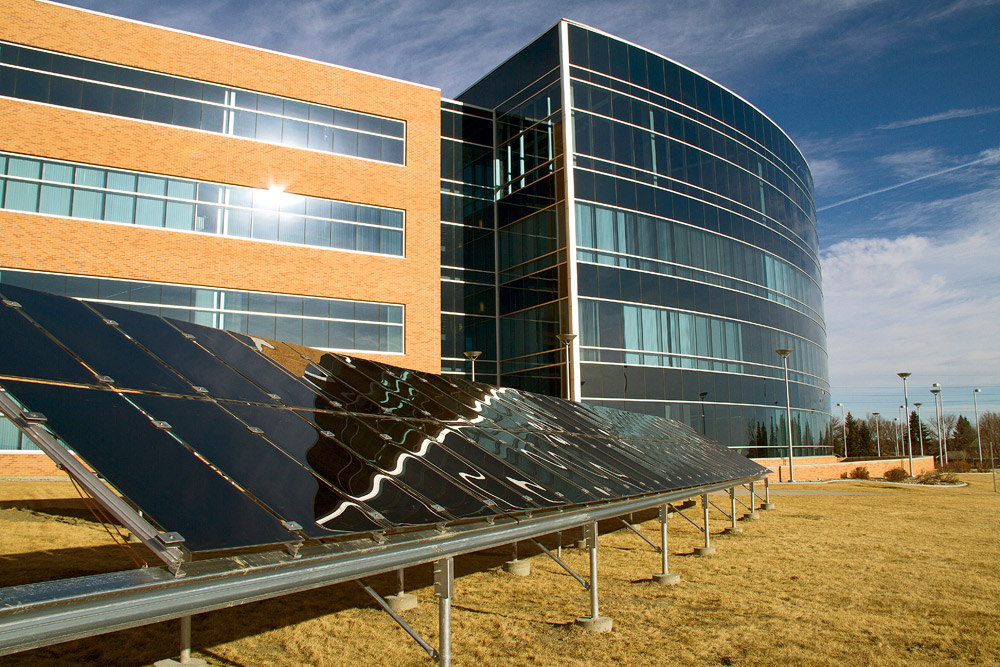

NECE Solar Panels: Bismarck State College has a large solar array for demonstration and educational purposes for students at the National Energy Center of Excellence. Photo courtesy of Bismarck State College National Energy Center of Excellence.
- Solar energy can provide water for cattle in areas where electricity is not available.
- No pollution is given off by solar power.
- North Dakota's solar energy industry has the potential to keep growing.
- North Dakota has more sunlight than many other states.
- North Dakota's long summer days could provide more solar electricity than places like Florida or Texas.
- More workers are needed in the field of solar energy and other renewable energy fields in North Dakota.