What petroleum and natural gas are:
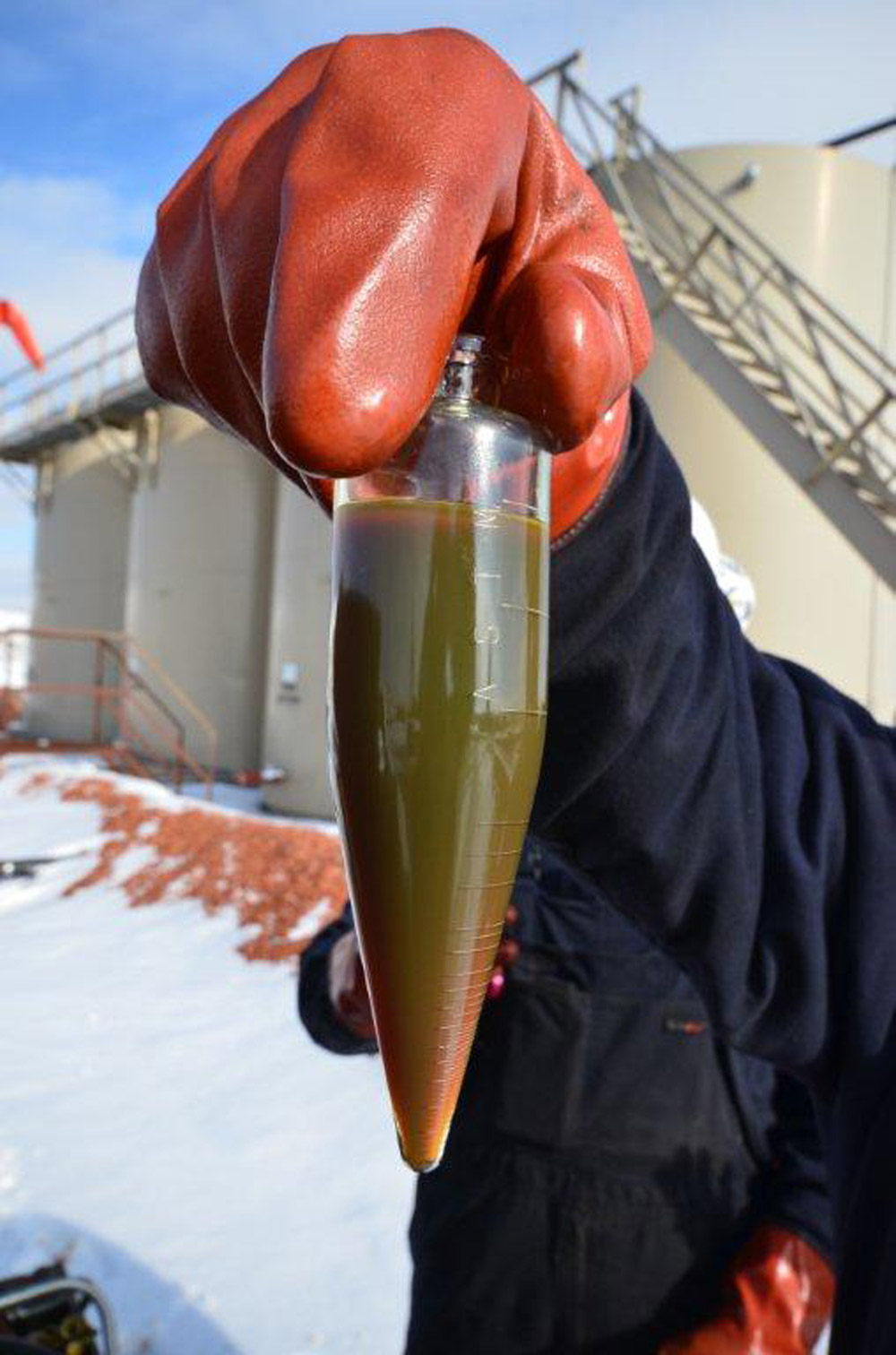

Bakken Oil: A worker holds a small container of Bakken oil. Photo courtesy of MBI Energy Services.
- PetroleumThe word petroleum was derived from Latin – petra = rock and oleum = oil (“rock oil”). is a flammable liquid mixture of hydrocarbons and other organic compounds found beneath the surface of the earth.
- Petroleum is commonly called crude oil or oil.
- Natural gas is a gaseous mixture of hydrocarbons, primarily methane, a colorless, odorless, flammable gas.
- A hydrocarbon is a combination of hydrogen and carbon molecules.
- Natural gas and petroleum are fossil fuels that are often found together.
- Natural gas is the cleanest-burning fossil fuel.
- Petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels. The other fossil fuel is coal. In North Dakota, oil and gas are found primarily in rocks that are 300 to 500 million years old. Lignite (a type of coal) in North Dakota is roughly 62 million years old. The North Dakota Geological Survey estimates that oil in the Bakken Formation began forming 70 million years ago.
How fossil fuels were formed:
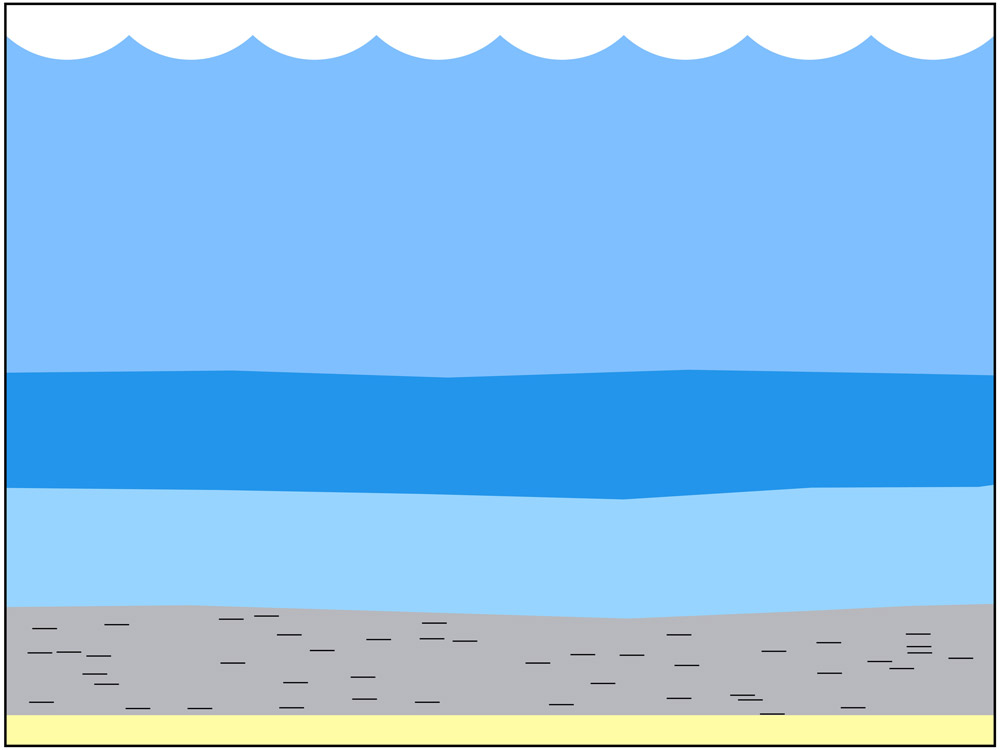
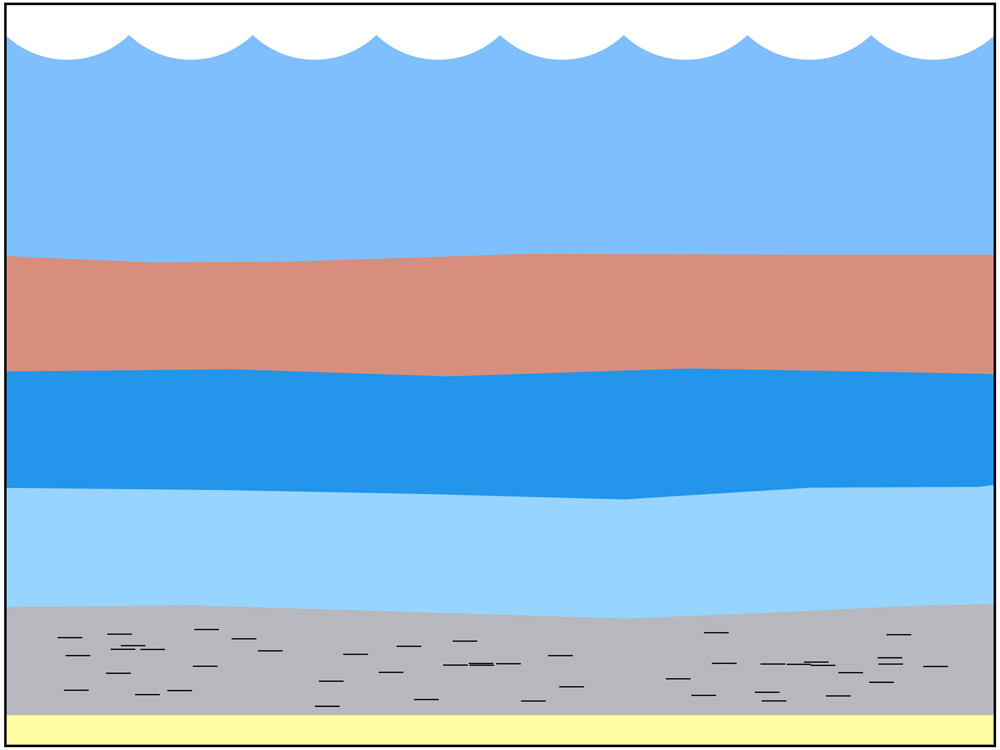
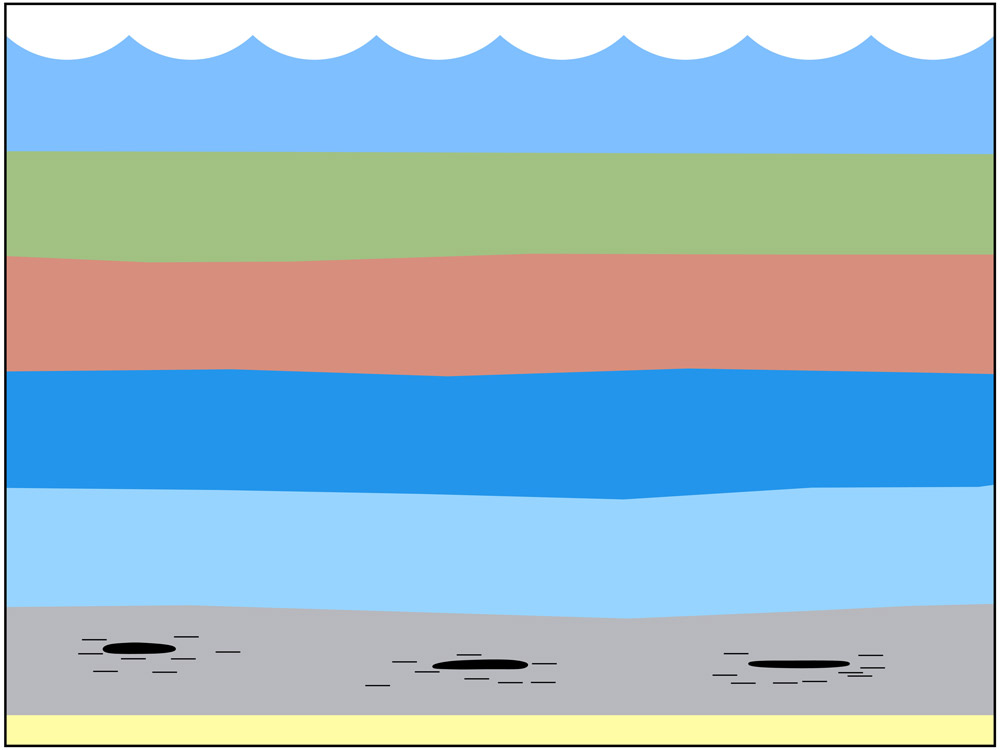
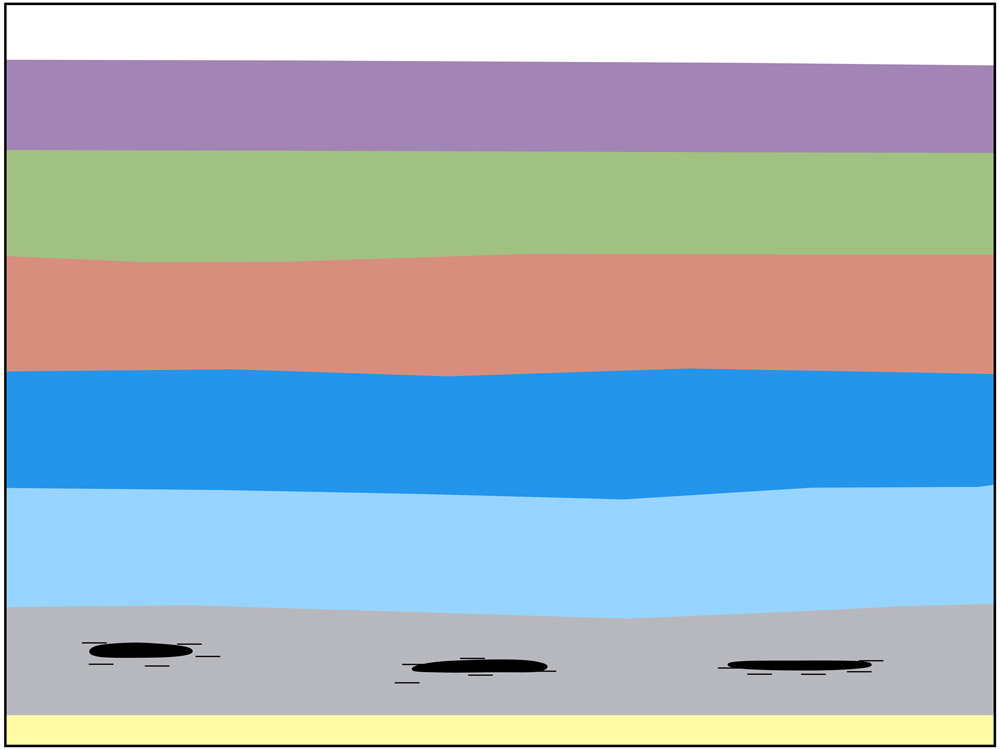
- Fossil fuels were created by anaerobic (without oxygen) decay of organic matter deep below the surface of the earth.
- Petroleum and natural gas were created from miniscule aquatic organisms such as zooplankton and algae. (Coal primarily formed from plants that grew on land.)
- The enormous weight and pressure, together with very high heat, “cooked” the marine organisms into the liquid called petroleum. As the heat increased, natural gas was created.