What solar power is:
- Solar power is power created by changing the energy of the sun’s rays into a useful form of energy.
- Solar energy is radiant energy produced in the core of the sun in a process called nuclear fusion.
- Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction in which hydrogen nuclei separate from their electrons and fuse together to form a heavier element.
-
In the sun, hydrogen combines to form helium.
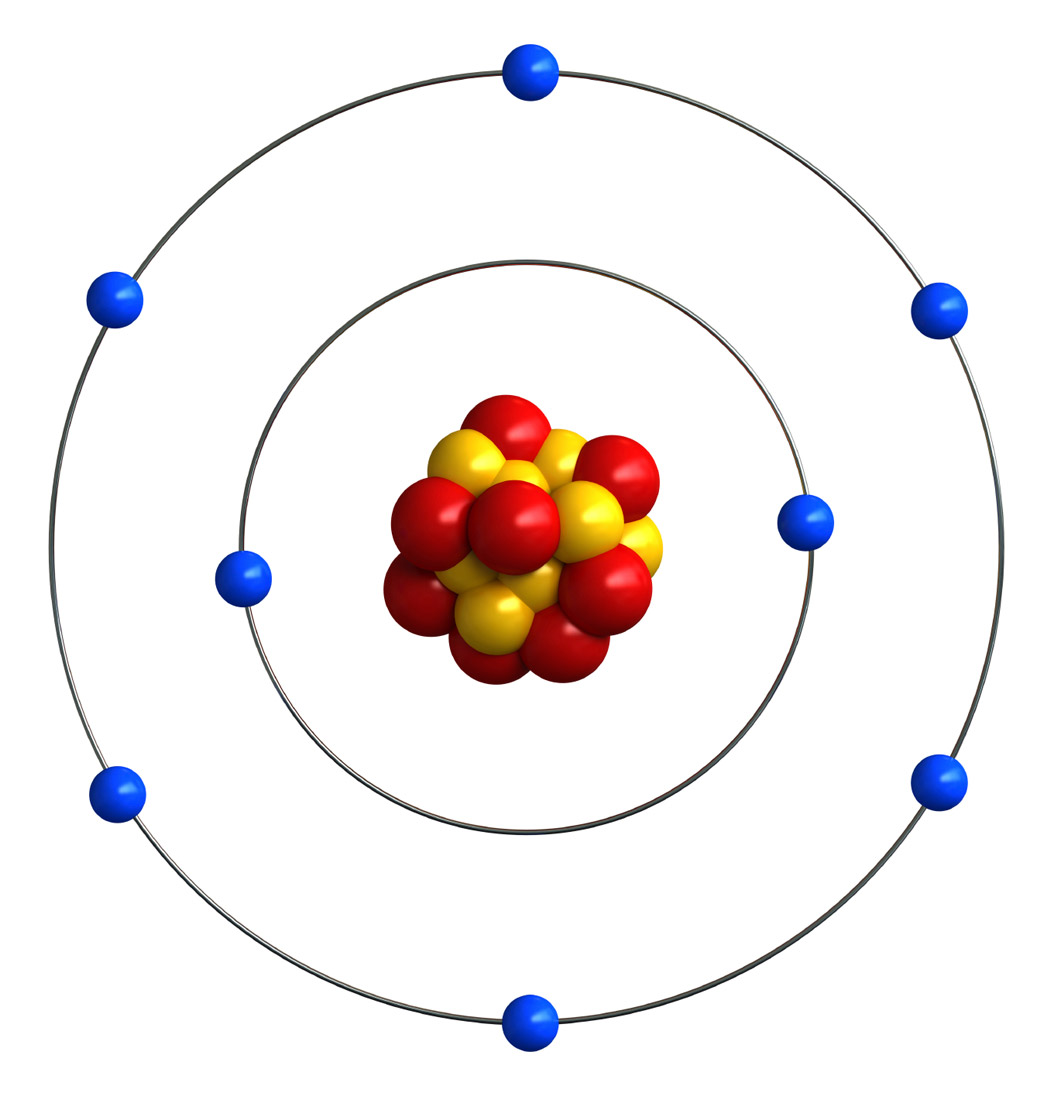 The nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus. (Nuclei is the plural of nucleus.)
The nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus. (Nuclei is the plural of nucleus.)
-
- The transmutation of matter (changing one element to another) results in some mass being lost. The lost matter is emitted into space as radiant energy.
- Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction in which hydrogen nuclei separate from their electrons and fuse together to form a heavier element.
Nuclear fusion occurs because the sun’s extremely high temperature and pressure cause the hydrogen nuclei to collide at very high speed and fuse together, forming a new type of atomic nucleus (helium).
- The energy created by nuclear fusion in the core of the sun can take 150,000 years to reach the surface of the sun.
- It takes about 8 minutes for solar energy to travel to the earth.
- The sun is 93 million miles from the earth, and solar energy travels at the speed of light (186,000 miles per second).
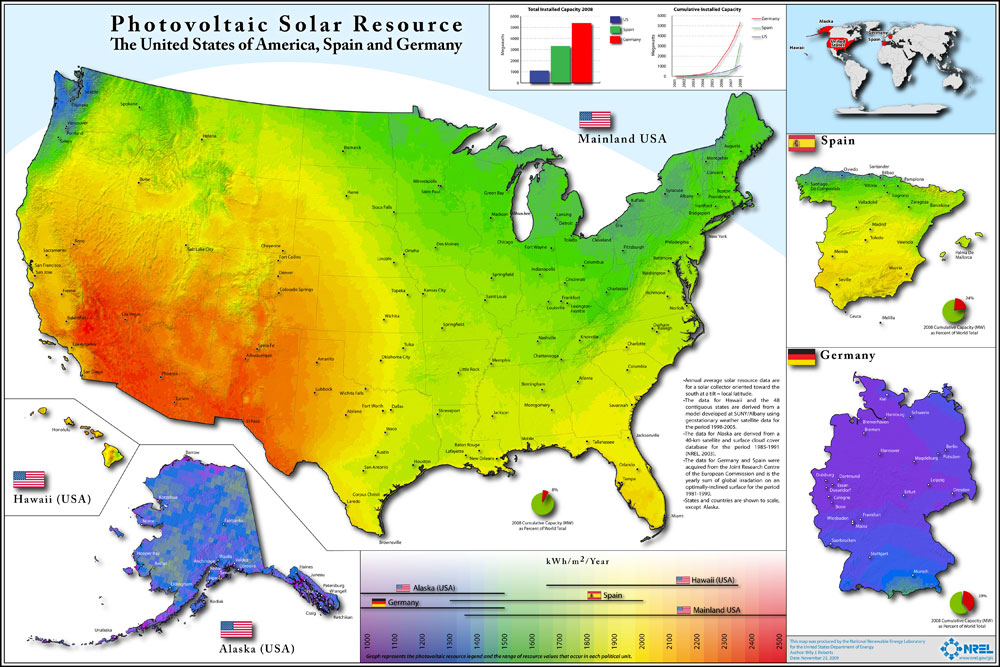
Solar Map US Spain Germany: This map indicates that solar radiation for North Dakota is equal to or better than that of Spain and Germany which rank respective as the world’s number three and number one countries for solar energy installations. This map was created by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory for the Department of Energy.
- According to geologist, Dr. Richard Alley, the sun’s radiation striking the earth’s surface has the energy equivalent of 26,000 TeraWatts (26 trillion watts).
- Of the solar energy that strikes the earth, about 30 percent is reflected back into space.
- Another 25 percent evaporates water, which produces rainfall.
- The remainder of the solar energy that reaches the earth is absorbed by plants, oceans, land; and used by animals and humans.
- Energy from the sun travels to the earth as photons, or light particles.
How solar power is used:
- Passive solar energy means that an object is heated because sunlight is warming it.
- Passive solar systems trap and store thermal energy directly from the sun.

An example of passive solar energy is sunlight passing through a home’s windows, which is then absorbed in the floors and walls. Also absorbent plates on a roof can heat liquid in tubes to supply a home with hot water.
- Electricity can be generated by solar energy in two ways – concentrated solar power and a photovoltaic system.
- Concentrated solar power (CSP) uses mirrors to concentrate the energy of the sun up to 2,000 times its normal intensity.
- Since CSP systems need a continuous supply of strong sunlight, this type of power has more potential for hot, dry regions such as deserts.
- A photovoltaicPhoto = light; volt is a measure of electricity. Photovoltaics (PV) literally means light electricity, or solar electricity (PV) system generates electricity directly from sunlight.
- Electricity is the flow of electrons.
- Electrons are the negatively-charged particles of an atom.
- A photovoltaic cell, commonly called a solar panel, is a silicon semiconductor.
- An example of this can be found on many calculators.
- Electricity is the flow of electrons.
- Concentrated solar power (CSP) uses mirrors to concentrate the energy of the sun up to 2,000 times its normal intensity.
Conductors, semiconductors, and insulators:
- Conductor: Material that electricity can flow through easily; copper is a common conductor.
- Semiconductor: Material that some electrical current is able to pass through in small amounts; most are made from silicon mixed with an impurity; all electronic devices use semiconductors.
- Insulator: Opposite of a conductor; does not allow electrons to flow easily from one atom to another; rubber, plastic, and glass are common insulating materials.
Ivanpah is the largest solar project currently operating in the U.S. Read more details about the project here (PDF).
- PV devices generate electricity directly from sunlight.
- Photons strike semiconductor material on a solar panel, which knocks electrons loose from their atoms.
- When electrons move, they cause an electric current.
Main components of a photovoltaic (PV) system:
- PV array: Composed of several panels made from individual solar cells grouped together.
- Batteries: Store excess energy to be used at night or when there is no other energy input.
- Inverter: Converts the direct current (DC power) that is generated by the PV cells into alternating current (AC power) so that it can be sent to the electricity grid.
- Utility meter: Tracks the amount of power that us being used.
- Wires and other parts.
- Visit the Bismarck State College Animation Tool to see how solar generation works.
Solar power in North Dakota:
- North Dakota has more hours of sunlight than any other state along the Canadian border.
- Solar energy is used in North Dakota for several purposes:
- For passive solar heat and daylighting;Daylighting means having windows, skylights, etc. placed so that natural light from the sun is used to help light the interior of the building.
- For solar thermal and hot water heat;
- To generate electricity by photovoltaic systems.
- Verendrye (ver-EN-dray) Electric Cooperative in Velva has the largest solar program in the state.
-
This utility company owns more than 260 solar-powered water pumps.
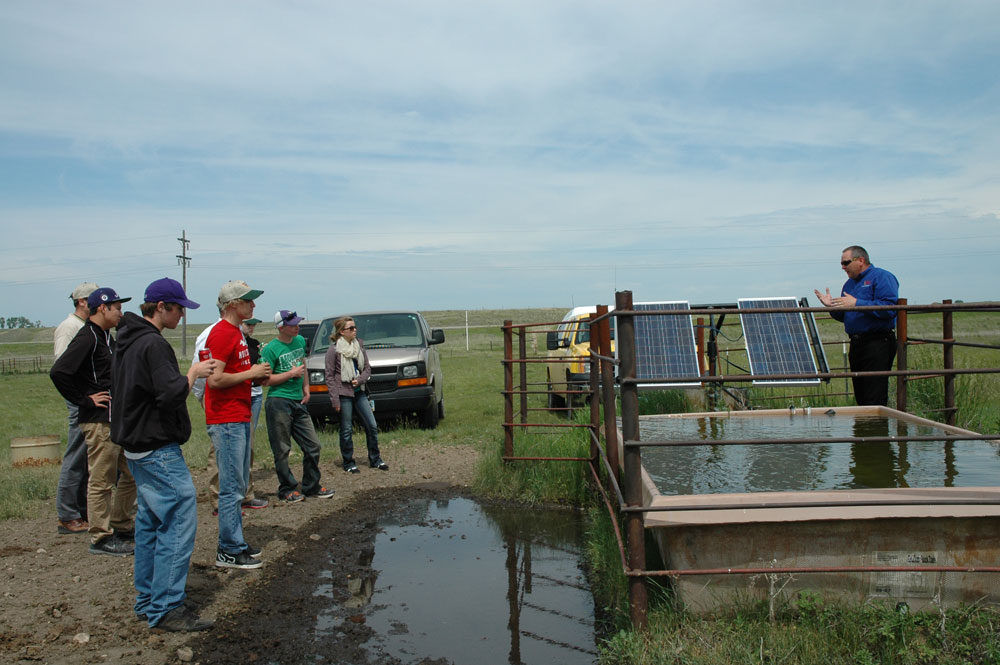 Tom Jespersen, energy advisor for Verendyre Electric teaches a group of high school students about solar panels Verendrye members use to power pumps to water cattle. Photo courtesy of Verendrye Electric Cooperative.
Tom Jespersen, energy advisor for Verendyre Electric teaches a group of high school students about solar panels Verendrye members use to power pumps to water cattle. Photo courtesy of Verendrye Electric Cooperative.- These pumps are used in pasture wells in remote areas far from power lines.
- Farmers using the solar pumps pay around $800 to install the pump and then $18 per month to lease the solar panels.
- This is a good deal for the farmer, since installing electrical power lines could cost as much as $15,000 per mile.
-
- Cass County Electric Cooperative in Fargo, N.D., installed a 102-kW solar array in 2016, called Prairie Sun Community Solar. It is the first community solar project in the state and consists of 324 solar panels located on land owned by the city of Fargo.
- The North Dakota Department of Commerce supports the following solar energy programs:
- Photovoltaic lighting for signs at Cross Ranch State Park, Turtle River State Park, and the State Hospital at Jamestown;
- A photovoltaic water pumping system at Cross Ranch State Park;
- A project by North Dakota Weatherization for solar thermal and hot water systems for homes;
- Passive solar designs for homes constructed by Bismarck State College (BSC) students in their carpentry program;
- Sponsoring teams from North Dakota universities that race solar-powered cars.
-
Bismarck state College has an 8 kW solar array (PV) for demonstration and educational purposes.
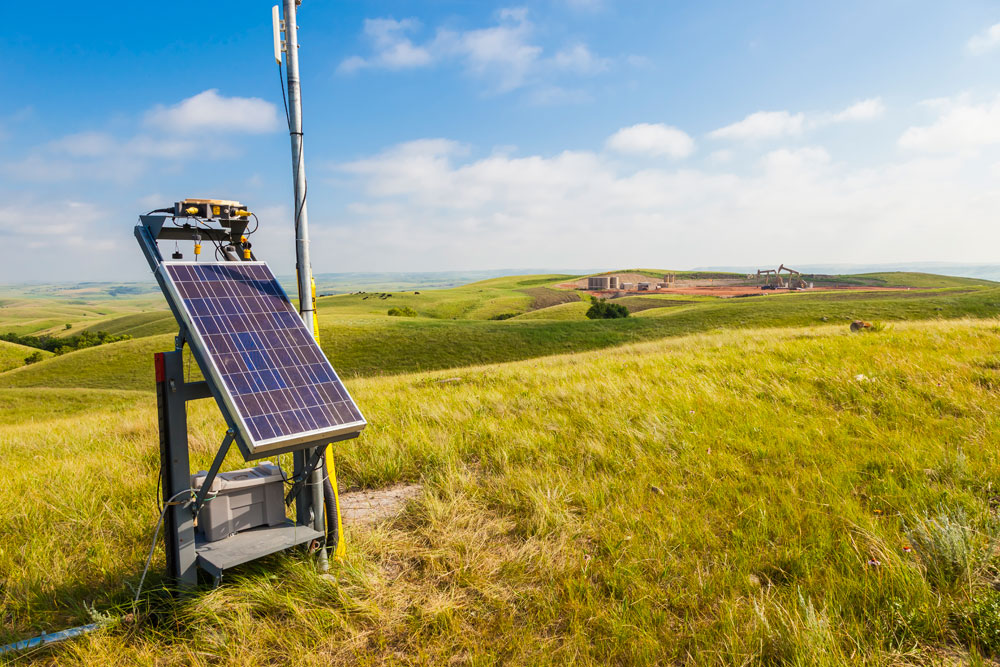 Whiting Petroleum PV array: Whiting Petroleum uses PV systems to power pumping units at oil well sites in remote areas far from power lines. Photo courtesy of Whiting Petroleum.
Whiting Petroleum PV array: Whiting Petroleum uses PV systems to power pumping units at oil well sites in remote areas far from power lines. Photo courtesy of Whiting Petroleum.
How solar power affects the people of North Dakota:
- Solar energy can provide water for cattle in areas where electricity is not available.
- No pollution is emitted by solar energy systems, and they have minimal impact on the environment.
-
North Dakota’s solar energy industry has the potential to keep growing.
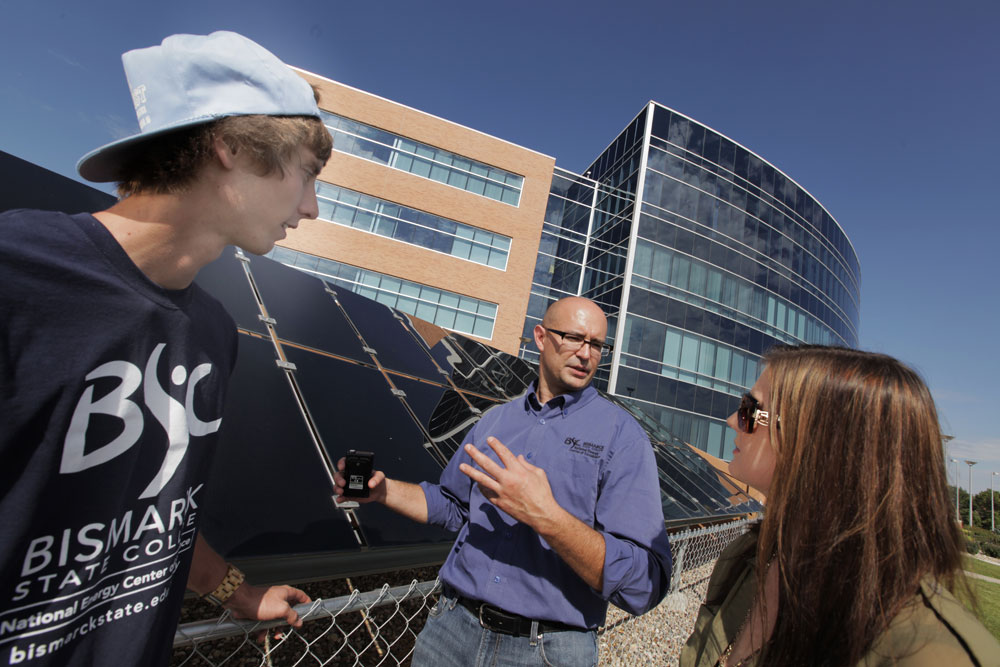 BSC Solar Students: Students at Bismarck State College National Energy Center of Excellence receive training on demonstration solar panels on campus. Photo courtesy of Bismarck State College.
BSC Solar Students: Students at Bismarck State College National Energy Center of Excellence receive training on demonstration solar panels on campus. Photo courtesy of Bismarck State College.- North Dakota has more sunlight than many other states.
- North Dakota’s long summer days could provide more solar electricity than places like Florida or Texas.
- More workers are needed in the field of solar energy and other renewable energy fields in North Dakota.
- North Dakota has more sunlight than many other states.